Day 29: Putting It All Together - Constructing a Stratified Audit Plan
Synthesize quantile thresholds, stratification, sample sizes, and investigation workflows into a complete audit plan.
We've built the mathematical foundations. Now it's time to assemble them into a complete stratified audit plan—from threshold computation to sample selection to investigation summary.
Note: This article uses technical terms and abbreviations. For definitions, check out the Key Terms & Glossary page.
The Goal: End-to-End Audit Plan
Objective: Design a stratified sampling plan that:
- Partitions population into meaningful strata
- Allocates samples optimally across strata
- Enables statistical inference about fraud rates
- Provides actionable investigation priorities
Key Components:
Threshold Computation → Stratification → Sample Sizing →
Selection → Investigation → Summary → Adjustment
Step 1: Threshold Computation
Using Quantile-Based Cutoffs
Approach: Use percentiles to define stratum boundaries.
Example: Transaction Amount Strata
Show code (9 lines)
# Compute percentile cutoffs
data = transactions['amount']
cutoffs = {
'Low': (0, np.percentile(data, 50)), # 0-50th percentile
'Medium': (np.percentile(data, 50), np.percentile(data, 85)), # 50-85th
'High': (np.percentile(data, 85), np.percentile(data, 99)), # 85-99th
'Extreme': (np.percentile(data, 99), np.inf) # 99th+
}
Result:
Show code (9 lines)
Stratum Range Count % of Population
Low $0 - $100 50,000 50%
Medium $100 - $500 35,000 35%
High $500 - $2,000 14,000 14%
Extreme $2,000+ 1,000 1%
Total 100,000 100%
Visual Example:
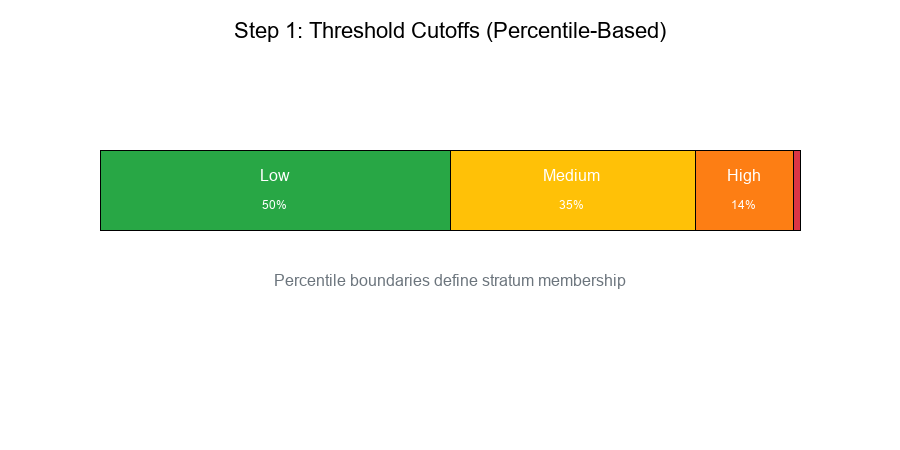
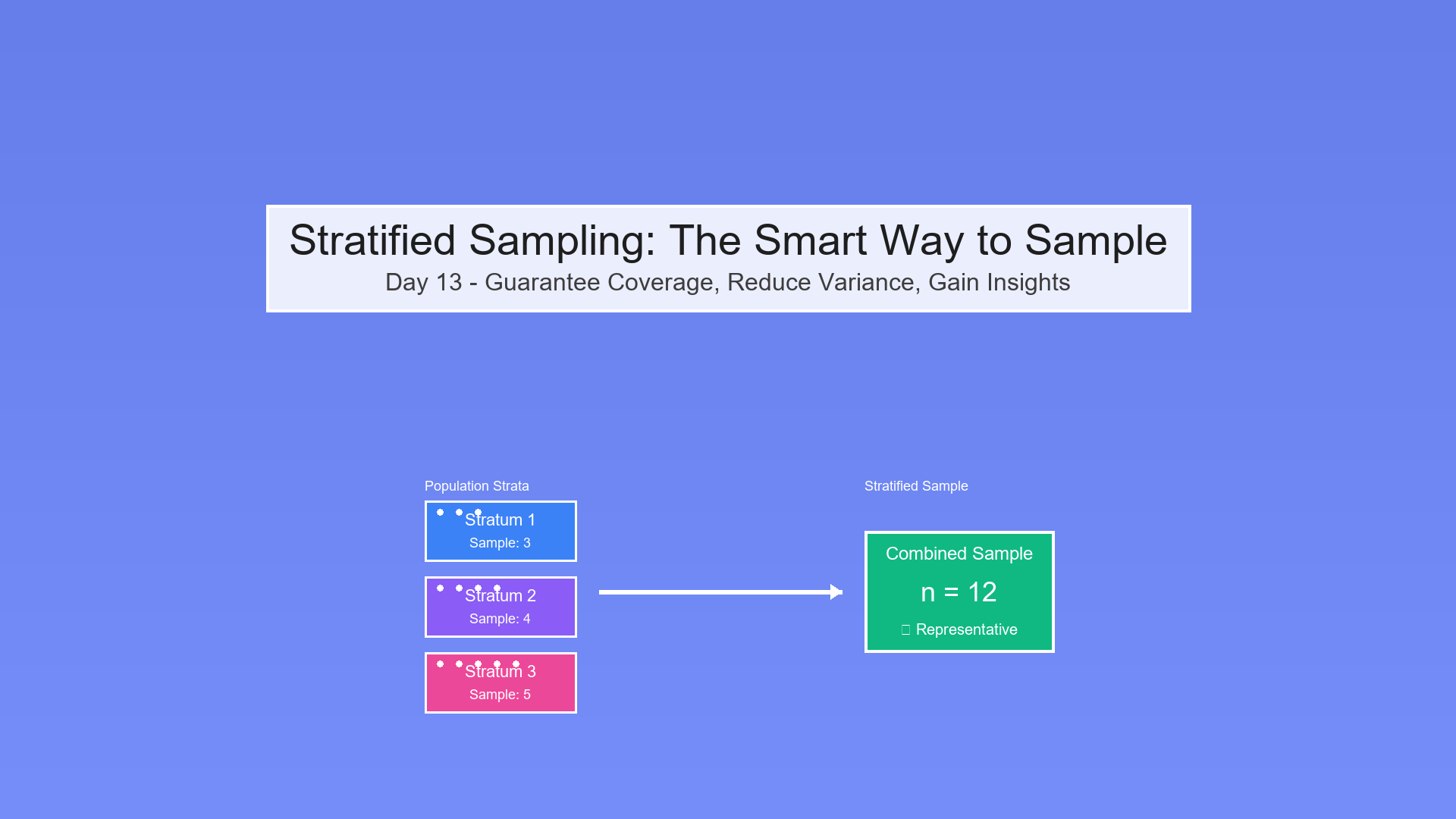
Step 2: Stratification Design
Combining Multiple Features
Multi-dimensional stratification:
Show code (14 lines)
def create_strata(df):
"""
Create strata based on multiple features.
"""
strata = []
for amount_level in ['Low', 'Medium', 'High', 'Extreme']:
for risk_level in ['Low', 'Medium', 'High']:
for account_age in ['New', 'Seasoned']:
stratum = f"{amount_level}_{risk_level}_{account_age}"
strata.append(stratum)
return strata # 4 × 3 × 2 = 24 strata
Stratum Characteristics
For each stratum, compute:
- Population size (N_h): Number of elements
- Expected fraud rate (p_h): Historical or estimated
- Variance (σ²_h): Variability within stratum
- Cost per sample (c_h): Investigation cost
Example Table:
Show code (9 lines)
Stratum N_h p_h σ²_h Priority
Extreme_High_New 200 0.15 0.13 Critical
Extreme_High_Seas 150 0.08 0.07 High
High_High_New 500 0.12 0.11 Critical
High_Medium_New 800 0.06 0.06 High
Medium_Low_Seas 10000 0.01 0.01 Routine
Low_Low_Seas 35000 0.002 0.002 Routine
Visual Example:

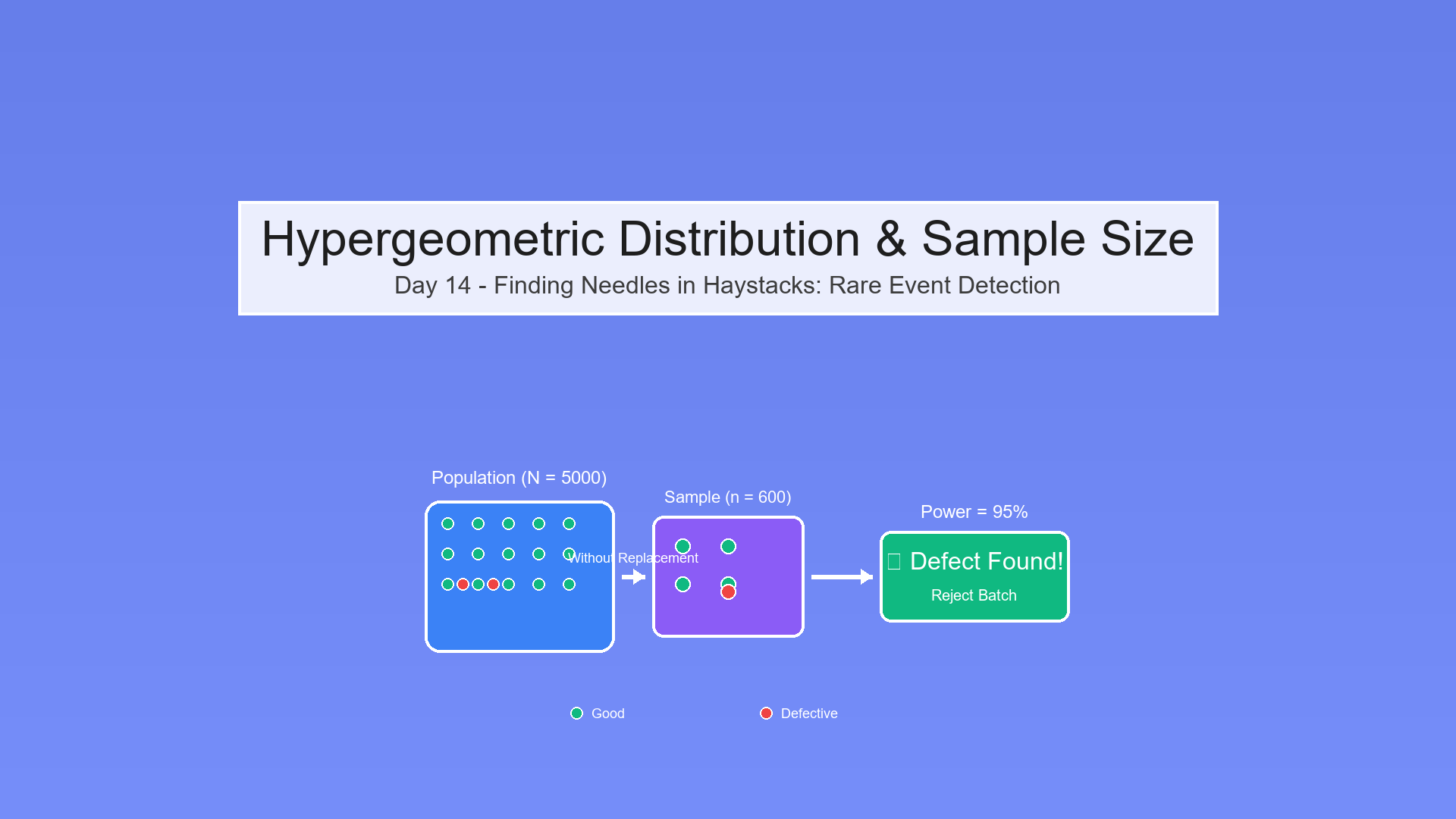
Step 3: Sample Size Determination
Power Analysis Framework
Goal: Determine sample size n_h for each stratum to detect fraud rate p_h with desired power.
Using Day 14 concepts:
Show code (21 lines)
def required_sample_size(p_h, p_0, alpha=0.05, power=0.80):
"""
Sample size for detecting deviation from baseline.
p_h: Expected fraud rate in stratum
p_0: Null hypothesis rate
alpha: Significance level
power: Desired power (1 - β)
"""
from scipy import stats
z_alpha = stats.norm.ppf(1 - alpha/2)
z_beta = stats.norm.ppf(power)
effect = p_h - p_0
pooled_var = p_h * (1 - p_h) + p_0 * (1 - p_0)
n = ((z_alpha + z_beta)**2 * pooled_var) / (effect**2)
return int(np.ceil(n))
Allocation Strategies
Proportional Allocation:
n_h = n × (N_h / N)
Neyman Allocation (optimal for variance):
n_h = n × (N_h × σ_h) / Σ(N_j × σ_j)
Risk-Weighted Allocation:
n_h = n × (N_h × p_h) / Σ(N_j × p_j)
Sample Size Table
Show code (11 lines)
Stratum N_h p_h Proportional Neyman Risk-Weighted
Extreme_High_New 200 0.15 2 15 50
Extreme_High_Seas 150 0.08 2 10 20
High_High_New 500 0.12 5 35 100
High_Medium_New 800 0.06 8 30 80
Medium_Low_Seas 10000 0.01 100 50 167
Low_Low_Seas 35000 0.002 350 20 117
Total Sample n - 467 160 534
Visual Example:

Step 4: Sample Selection
Random Selection Within Strata
Show code (20 lines)
def select_stratified_sample(df, strata_col, sample_sizes):
"""
Select random samples from each stratum.
"""
samples = []
for stratum, n in sample_sizes.items():
stratum_data = df[df[strata_col] == stratum]
if len(stratum_data) <= n:
# Take all if stratum is small
sample = stratum_data
else:
# Random sample
sample = stratum_data.sample(n=n, random_state=42)
samples.append(sample)
return pd.concat(samples)
Selection Tracking
selection_log = {
'stratum': [],
'population_size': [],
'sample_size': [],
'sampling_fraction': [],
'selection_date': [],
}
Step 5: Investigation Workflow
Investigation Priority Queue
Show code (22 lines)
def prioritize_investigations(sample, priority_rules):
"""
Assign investigation priority based on rules.
"""
priorities = []
for idx, row in sample.iterrows():
# Apply priority rules
if row['stratum'].startswith('Extreme_High'):
priority = 1 # Immediate
elif row['stratum'].startswith('High_High'):
priority = 2 # Urgent
elif 'High' in row['stratum']:
priority = 3 # Standard
else:
priority = 4 # Routine
priorities.append(priority)
sample['priority'] = priorities
return sample.sort_values('priority')
Investigation Outcomes
Track for each case:
- Confirmed Fraud (True Positive)
- Legitimate (False Positive)
- Inconclusive
- Time to resolution
Step 6: Summary and Reporting
Stratum-Level Summary
Show code (15 lines)
def investigation_summary(results):
"""
Summarize investigation results by stratum.
"""
summary = results.groupby('stratum').agg({
'is_fraud': ['sum', 'count', 'mean'],
'amount': 'sum',
'resolution_hours': 'mean'
})
summary.columns = ['fraud_count', 'total_reviewed',
'fraud_rate', 'total_amount', 'avg_hours']
return summary
Example Summary Report
Show code (11 lines)
Stratum Reviewed Fraud Rate Amount Avg Hours
Extreme_High_New 50 8 16.0% $125,000 2.5
Extreme_High_Seas 20 2 10.0% $45,000 2.0
High_High_New 100 10 10.0% $280,000 3.0
High_Medium_New 80 4 5.0% $150,000 2.5
Medium_Low_Seas 167 2 1.2% $200,000 1.5
Low_Low_Seas 117 0 0.0% $80,000 1.0
TOTAL 534 26 4.9% $880,000 2.1
Visual Example:

Step 7: Overlay Adjustments
Using Results to Refine Thresholds
Based on investigation findings:
- Adjust cutoffs if fraud rates differ from expected
- Reallocate samples to high-yield strata
- Update priority rules based on actual outcomes
- Refine feature selection for stratification
Adjustment Framework
Show code (25 lines)
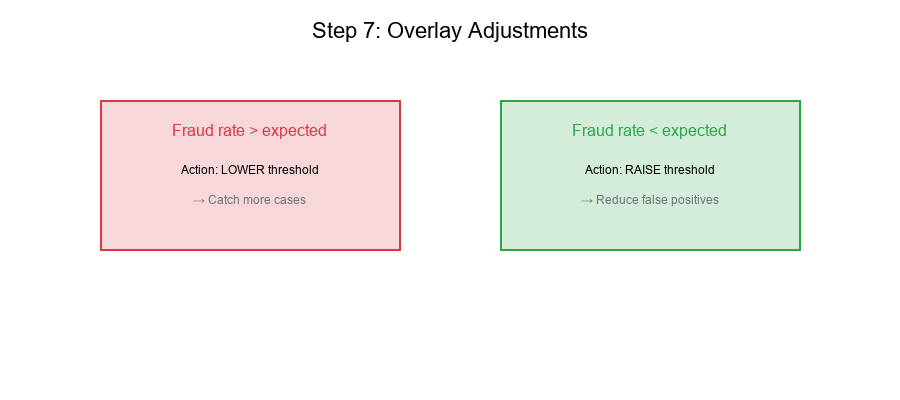
def suggest_adjustments(summary, expectations):
"""
Suggest threshold adjustments based on results.
"""
adjustments = []
for stratum, row in summary.iterrows():
expected = expectations.get(stratum, {}).get('fraud_rate', 0.05)
actual = row['fraud_rate']
if actual > expected * 1.5:
adjustments.append({
'stratum': stratum,
'action': 'LOWER_THRESHOLD',
'reason': f'Fraud rate {actual:.1%} >> expected {expected:.1%}'
})
elif actual < expected * 0.5:
adjustments.append({
'stratum': stratum,
'action': 'RAISE_THRESHOLD',
'reason': f'Fraud rate {actual:.1%} << expected {expected:.1%}'
})
return adjustments
Visual Example:
Exercise: Design a Three-Strata Plan
The Problem
Given: A mock feature "transaction_velocity" (transactions per hour)
Design: A three-strata audit plan with:
- Cutoffs (percentile-based)
- Sample sizes (power-based)
- Expected outcomes
Solution
Step 1: Analyze Feature Distribution
velocity_data = [0.5, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 10, 15, 20, 50, ...] # n = 10,000
Compute percentiles:
p50 = 5 transactions/hour
p85 = 15 transactions/hour
p99 = 50 transactions/hour
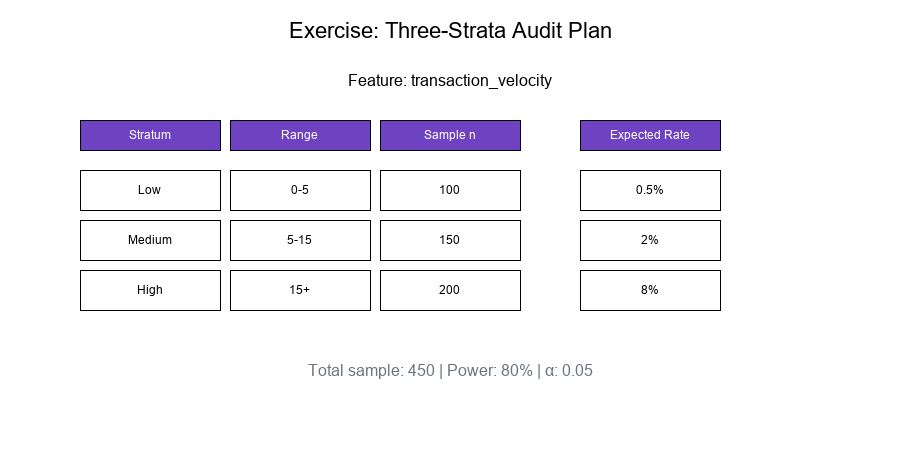
Step 2: Define Strata
| Stratum | Range | N_h | Expected p_h | |---------|-------|-----|--------------| | Low | 0 - 5 | 5,000 | 0.5% | | Medium | 5 - 15 | 3,500 | 2% | | High | 15+ | 1,500 | 8% |
Step 3: Compute Sample Sizes
Using power = 80%, α = 0.05, detecting p_h vs p_0 = 0.5%:
Low: n = 100 (confirm low rate)
Medium: n = 150 (detect elevation)
High: n = 200 (estimate accurately)
Total: n = 450
Step 4: Expected Outcomes
Stratum Sample Expected Fraud Expected Rate
Low 100 0-1 ~0.5%
Medium 150 2-4 ~2%
High 200 14-18 ~8%
Total 450 16-23 ~4%
Step 5: Document the Plan
Show code (14 lines)
audit_plan = {
'feature': 'transaction_velocity',
'strata': [
{'name': 'Low', 'range': (0, 5), 'n': 100, 'priority': 3},
{'name': 'Medium', 'range': (5, 15), 'n': 150, 'priority': 2},
{'name': 'High', 'range': (15, np.inf), 'n': 200, 'priority': 1}
],
'total_sample': 450,
'power': 0.80,
'alpha': 0.05,
'version': '1.0',
'created': '2025-11-29'
}
Visual Example:
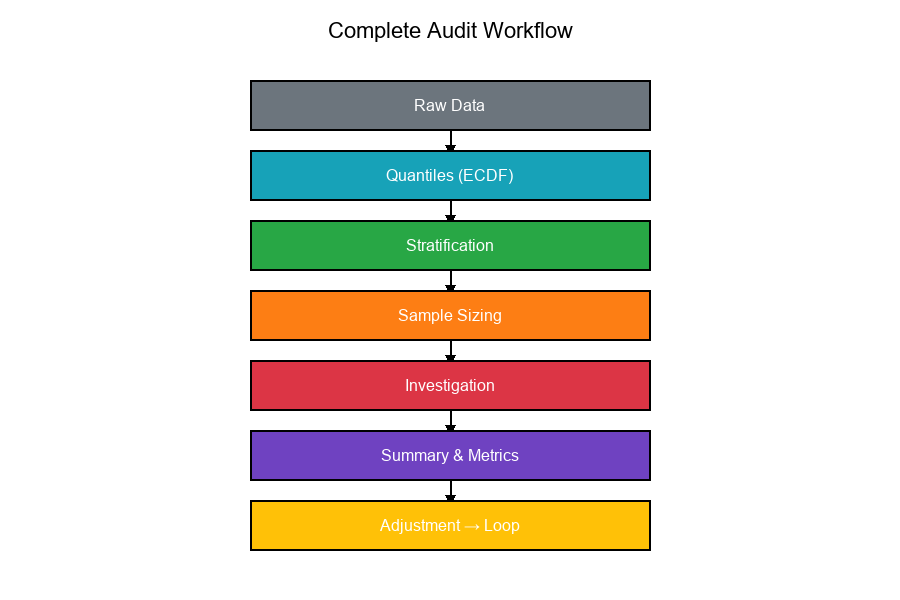
Complete Workflow Flowchart
Show code (20 lines)
Raw Data
Compute Quantiles Day 13-15: Percentiles, ECDF
Define Strata Day 23-24: Partitioning, Risk Levels
Compute Sample Day 14: Power Analysis
Sizes
Select Samples Day 16: Hypergeometric Sampling
Investigate
Summarize Results Day 18: F1 Score, Metrics
Adjust Thresholds Day 22: Set Overlap Analysis
Loop back to refine
Visual Example:
Summary Table
| Step | Input | Output | Key Concepts |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Thresholds | Raw data | Percentile cutoffs | Quantiles, ECDF |
| 2. Stratification | Cutoffs | Strata definitions | Partitioning |
| 3. Sample Sizing | Strata, power | n per stratum | Power analysis |
| 4. Selection | Population | Sample | Random sampling |
| 5. Investigation | Sample | Outcomes | Priority queue |
| 6. Summary | Outcomes | Report | Rates, metrics |
| 7. Adjustment | Report | New thresholds | Feedback loop |
Final Thoughts
A stratified audit plan is the culmination of all our mathematical tools:
- Quantiles define stratum boundaries
- Power analysis determines sample sizes
- Stratification enables targeted investigation
- Metrics measure effectiveness
- Feedback loops enable continuous improvement
Key Takeaways:
Quantile thresholds create meaningful strata Sample allocation balances precision and cost Power analysis ensures detectable differences Investigation priority focuses resources Summary reporting enables decisions Overlay adjustments close the loop
Plan stratified, investigate smart!
Tomorrow's Preview: Day 30 - A Mathematical Blueprint for Scenario Calibration